Working with Arduino
This chapter includes the following sections, please read as needed:
Arduino Getting Started Tutorial
New to Arduino ESP32 development and looking for a quick start? We have prepared a comprehensive Getting Started Tutorial for you.
- Section 0: Getting to Know ESP32
- Section 1: Installing and Configuring Arduino IDE
- Section 2: Arduino Basics
- Section 3: Digital Output/Input
- Section 4: Analog Input
- Section 5: Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)
- Section 6: Serial Communication (UART)
- Section 7: I2C Communication
- Section 8: SPI Communication
- Section 9: Wi-Fi Basics
- Section 10: Web Server
- Section 11: Bluetooth
- Section 12: LVGL GUI Development
- Section 13: Comprehensive Project
Note: This tutorial uses the ESP32-S3-Zero as a reference example, and all hardware code is based on its pinout. Before you start, we recommend checking the pinout of your development board to ensure the pin configuration is correct.
Setting Up Development Environment
1. Installing and Configuring Arduino IDE
Please refer to the tutorial Installing and Configuring Arduino IDE Tutorial to download and install the Arduino IDE and add ESP32 support.
2. Installing Libraries
- When installing Arduino libraries, there are typically two methods: Online Installation and Offline Installation. If the library installation requires offline installation, you must use the provided library file.
- For most libraries, users can easily search and install them through the online Library Manager in the Arduino software. However, some open-source libraries or custom libraries are not synchronized to the Arduino Library Manager, so they cannot be acquired through online searches. In this case, users can only manually install these libraries offline.
You can click this link to download the demo package for the ESP32-C6-LCD-1.3 board from the
Arduinodirectory. TheArduino\librariesdirectory within the package already includes all the library files required for this tutorial.
| Library/File Name | Description | Version | Installation Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adafruit_GFX_Library | Low-level graphics rendering library | v1.11.9 | Install via library manager or manually |
| Arduino_GFX | Display driver graphics library supporting ST7789 chip | v1.4.9 | Install via library manager or manually |
| ArduinoJson | Lightweight JSON parsing/generation library | v6.21.2 | Install via library manager or manually |
| lvgl | LVGL display framework | v8.3.10 | Install via library manager or manually |
| FastLED | Addressable LED control library | v3.10.3 | Install via library manager or manually |
| JPEGDEC | JPEG image decoding library | v1.6.1 | Install via library manager or manually |
| PNGdec | PNG image decoding library | v1.0.2 | Install via library manager or manually |
| Time | Basic time handling library | 1.6.1 | Install via library manager or manually |
| TJpg_Decoder | Ultra-lightweight JPEG decoding library | 1.0.8 | Install via library manager or manually |
There are strong dependencies between versions of LVGL and its driver libraries. For example, a driver written for LVGL v8 may not be compatible with LVGL v9. To ensure stable reproduction of the examples, it is recommended to use the specific versions listed in the table above. Mixing different library versions may cause compilation failures or runtime exceptions.
Installation Steps:
-
Download the demo package.
-
Copy all folders (Arduino_DriveBus, GFX_Library_for_Arduino, etc.) in the
Arduino\librariesdirectory to the Arduino library folder.infoThe path to the Arduino libraries folder is typically:
c:\Users\<Username>\Documents\Arduino\libraries.You can also locate it within the Arduino IDE via File > Preferences, by checking the "Sketchbook location". The library folder is the
librariesfolder under this path. -
For other installation methods, please refer to: Arduino Library Management Tutorial.
3. Installing ESP32 Development Board
- To use ESP32-related boards in the Arduino IDE, you must first install the board package "esp32 by Espressif Systems".
- According to board installation requirement''', it is generally recommended to use '''Install Online'''. If online installation fails, use '''Install Offline'''.
- For the installation tutorial, please refer to Arduino Board Management Tutorial
Required Board Installation Instructions for ESP32-C6-LCD-1.3
| Board Name | Installation Requirement | Version Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| ESP32 by Espressif Systems | "Install Offline" / "Install Online” | 3.0.1 |
Demo
The Arduino demos are located in the Arduino/examples directory of the demo package.
| Demo | Basic Program Description | Dependency Library |
|---|---|---|
| 01_LVGL_Arduino | Demonstrates basic graphics library functions, hardware parameter detection, and display | FastLED, lvgl |
| 02_LVGL_WeatherClock | Demonstrates basic graphics library functions, can also be used to test basic display performance and random text display effects | GFX_Library_for_Arduino, Arduino_DriveBus, Adafruit_XCA9554 |
| 03_Video_demo | Prints ASCII characters in rows and columns on the display according to the screen size | GFX_Library_for_Arduino |
ESP32-C6-LCD-1.3 Model Selection
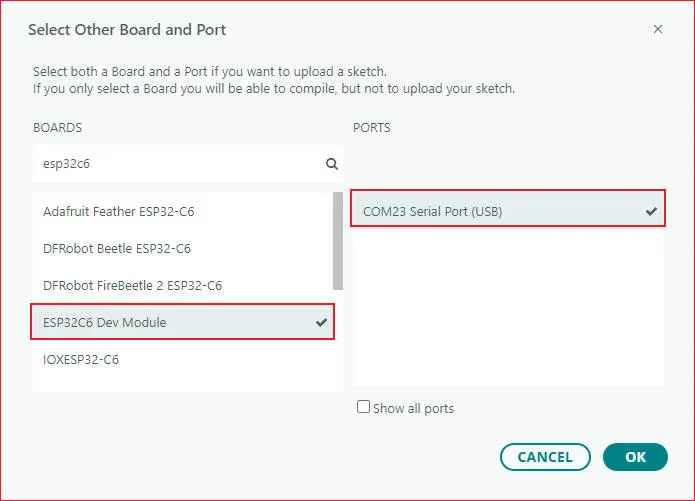
01_LVGL_Arduino
Demo Description
- This example demonstrates displaying hardware information (Flash/TF card capacity, number of scanned wireless devices) through an LVGL graphical interface.
Hardware Connection
- Connect the development board to the computer
Code Analysis
setup()function:Flash_test(): Detects the ESP32 Flash chip capacity and assigns it to the global variableFlash_Size.LCD_Init(): Initializes the ST7789 display (configures SPI, screen commands, backlight, etc.).Lvgl_Init(): Initializes the LVGL graphics library, binds the ST7789 display refresh function, creates a basic LVGL display buffer, and registers touch (placeholder) and display drivers.SD_Init(): Initializes the TF card, detects the card type, calculates the total capacity, and assigns it toSDCard_Size.Lvgl_Example1(): Creates the LVGL interface (Onboard parameter panel), initializes WS2812B and the waterfull light / button.Wireless_Test2(): Creates the FreeRTOS taskWirelessScanTask, which runs in the background on core 0 to scan for WiFi/BLE devices, and stores the results inWIFI_NUM/BLE_NUM.
loop()function:Timer_Loop(): Calls the LVGL core timer handlerlv_timer_handler()to maintain interface refresh and normal execution of timers (such as button detection, waterfull light, parameter refresh).delay(5): A simple delay to ensure LVGL refresh rate.
Operation Result
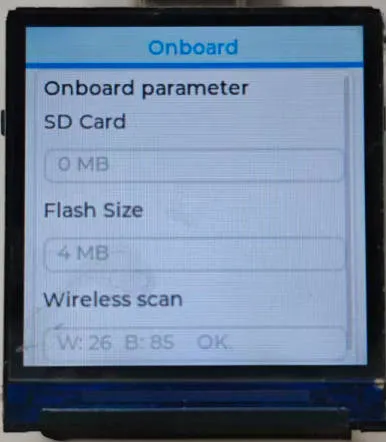
02_LVGL_WeatherClock
Demo Description
- This example demonstrates a weather clock system, presenting weather clock functionality on the ST7789 display while optimizing for smooth operation and CPU resource usage.
Hardware Connection
- Connect the development board to the computer
Code Analysis
setupfunction:- Serial Initialization: Enables serial communication at 115200 baud for system log printing, facilitating debugging.
- Hardware/Driver Initialization: Executes Flash test, ST7789 display initialization, LVGL graphics library initialization, and TF card initialization in sequence.
- Peripheral Configuration: Sets the display backlight to 100% and initializes the weather clock business logic.
- Log Output: Provides initialization progress feedback via serial, facilitating troubleshooting of startup anomalies.
loopfunction:- LVGL Core Processing: Calls
Timer_Loopto ensure LVGL timers and animations update normally. - Business Logic Loop: Executes
WeatherClock_Loopto handle real-time data updates and display logic for the weather clock. - Resource Optimization: Retains only a 1ms delay, avoiding excessive CPU usage while ensuring high-frequency LVGL scheduling, balancing smoothness and resource consumption.
- LVGL Core Processing: Calls
Operation Result
 | 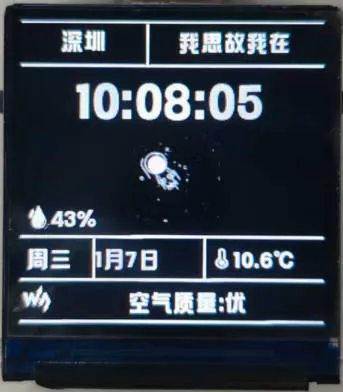 |
|---|
03_Video_demo
Demo Description
- This example demonstrates TF card detection and video multimedia playback.
Hardware Connection
- Connect the development board to the computer
Code Analysis
setup()function:- Hardware Initialization: Completes Flash test, ST7789 display initialization, backlight setting, and WS2812B LED strip initialization in sequence.
- RGB Self-Test: Sequentially displays red/green/blue colors simultaneously on the screen and LED strip, holding each for 1 second before turning off the LED strip.
- TF Card Detection: Identifies the TF card type. If no card is found, an error message is displayed on the screen and subsequent processes are terminated. If a card is present, it checks for video files. If a video file exists, the video playback module is initialized.
loop()function:- Fallback Logic: If no TF card is detected, only delays in the loop without executing any playback operations.
- Playback Branch: If the video module is initialized, calls
Video_Play_Loop()to play the video in a loop.
Operation Result
 |
|---|