SOS Signal
The core logic of this tutorial applies to all ESP32 development boards. However, all operational steps are explained using the Waveshare ESP32-S3-Zero Mini Development Board as an example. If you are using a different model of development board, please modify the relevant settings according to your actual situation.
Project Introduction
This project demonstrates a simulation of an SOS signal. It controls an LED and a buzzer via the GPIO pins of an ESP32 to simulate the SOS signal in Morse code.
Morse Code
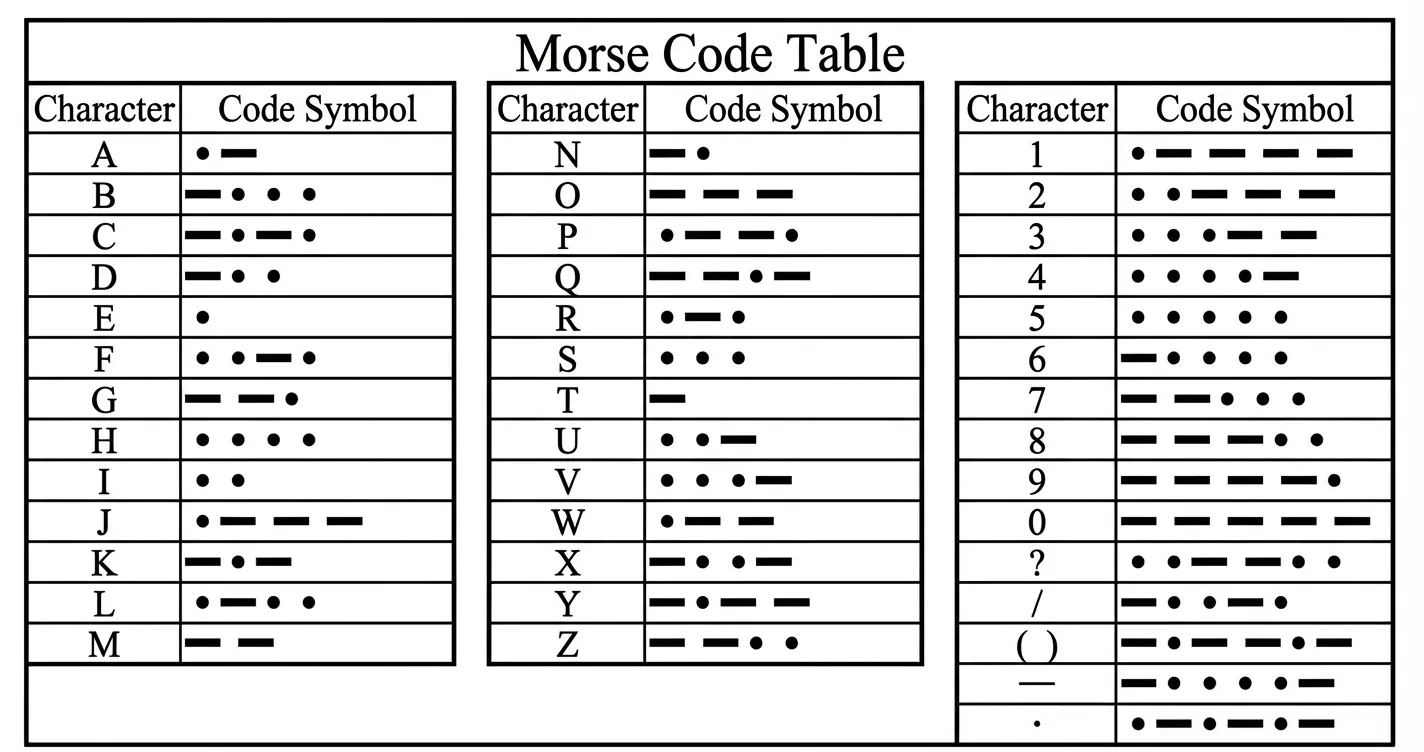
First, let's understand the rules of Morse Code. Morse code expresses different letters, numbers, and punctuation marks by arranging basic signals in different sequences. It primarily consists of two fundamental signals:
- Dot: A short signal, denoted as
. - Dash: A long signal, denoted as
-
This project simulates the internationally recognized distress signal SOS. Its encoding rules are as follows:
- S: Composed of 3 dots, i.e.,
... - O: Composed of 3 dashes, i.e.,
---
Therefore, the entire transmission sequence for the SOS signal is: ... --- ....
Timing Definitions:
Understanding the character composition is not enough; we also need to strictly adhere to the international standard timing ratios, which dictates the numerical relationships of the variables in our code:
- Base Unit: We define the duration of a "dot" as 1 time unit (1t).
- Dash Length: Is 3 times the length of a dot (3t).
- Interval Timing:
- Intra-character Gap: The pause between dots and dashes within the same letter is 1t.
- Inter-letter Gap: The pause between letters is 3t.
- Inter-word Gap: The pause between words (or SOS sequences) is 7t.
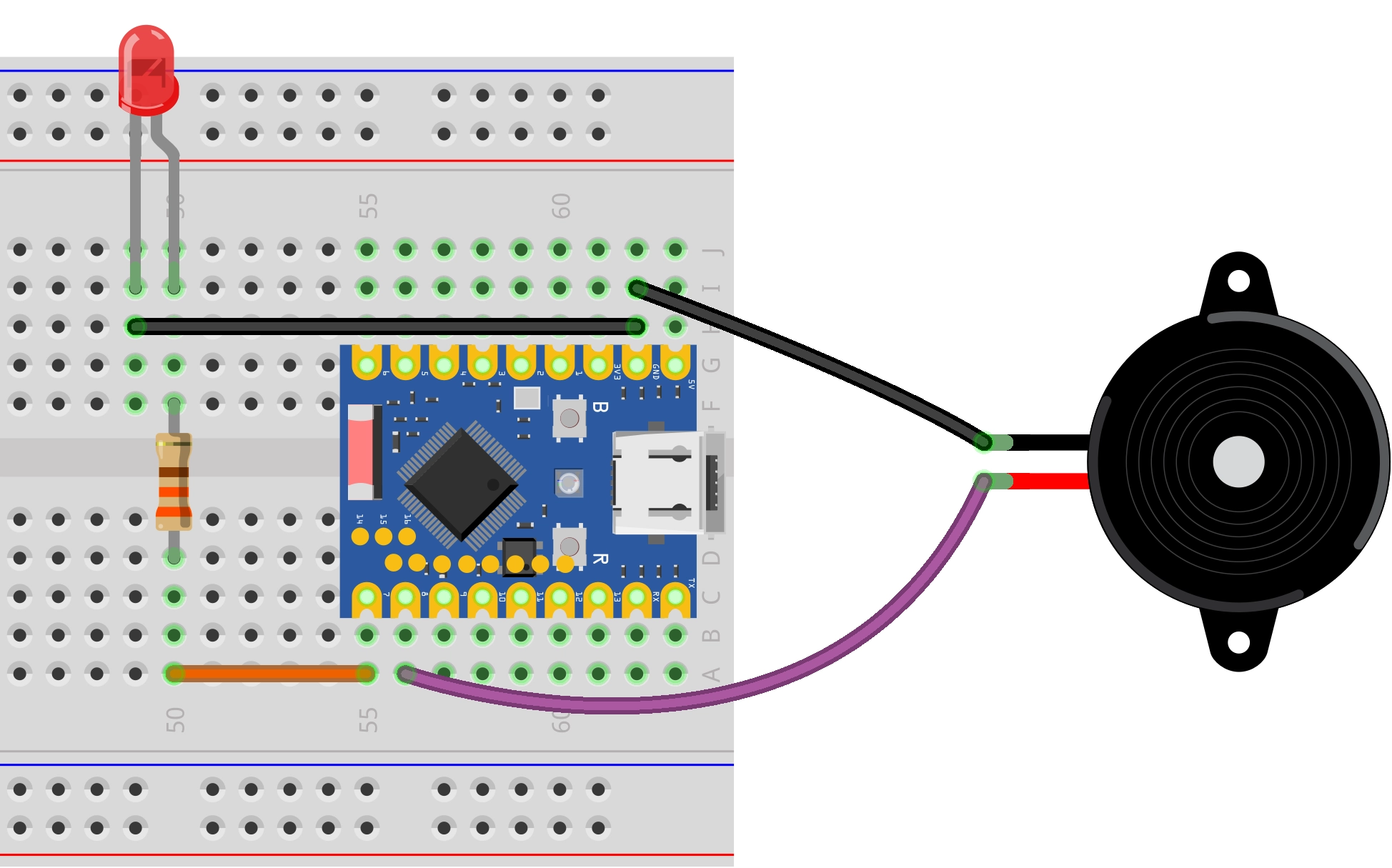
Hardware Connection
The components required are:
- LED * 1
- 330Ω resistor * 3
- Active buzzer * 1
- Breadboard * 1
- Wire
- ESP32 development board
Connect the circuit according to the wiring diagram below:
ESP32-S3-Zero Pinout Diagram

Code Implementation
/*
SOS Signal
Simulates an SOS signal using an LED and a buzzer.
Hardware:
- LED connected to pin 7
- Buzzer connected to pin 8
Wulu (Waveshare Team)
*/
// Define pins for LED and Buzzer
const int ledPin = 7;
const int buzzerPin = 8;
// --- Morse Code Timing Definitions (unit: milliseconds) ---
const int dotDuration = 200; // "Dot" duration (1t)
const int dashDuration = dotDuration * 3; // "Dash" duration (3t)
const int interElementGap = dotDuration; // Gap between elements of a letter (1t)
const int interLetterGap = dotDuration * 3; // Gap between letters (3t)
const int interWordGap = dotDuration * 7; // Gap between SOS sequences (7t)
// Function Declarations
void signalOn();
void signalOff();
void dot();
void dash();
void letterS();
void letterO();
void playSOS();
void setup() {
// Initialize serial communication
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Program started, preparing to transmit SOS signal...");
// Configure pins as OUTPUT
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(buzzerPin, OUTPUT);
// Ensure devices are initially off
signalOff();
delay(2000); // Wait 2 seconds before starting
}
void loop() {
playSOS();
// After a complete SOS sequence, wait for the inter-word gap
Serial.print("Waiting ");
Serial.print(interWordGap);
Serial.println(" milliseconds before repeating...\n");
delay(interWordGap);
}
// --- Core Function Definitions ---
// Turn on both LED and Buzzer simultaneously
void signalOn() {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH);
digitalWrite(buzzerPin, HIGH);
}
// Turn off both LED and Buzzer simultaneously
void signalOff() {
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW);
digitalWrite(buzzerPin, LOW);
}
// Transmit a "dot" signal
void dot() {
signalOn();
delay(dotDuration);
signalOff();
}
// Transmit a "dash" signal
void dash() {
signalOn();
delay(dashDuration);
signalOff();
}
// Transmit the letter 'S' (...): three dots
void letterS() {
Serial.print(".");
dot();
delay(interElementGap);
Serial.print(".");
dot();
delay(interElementGap);
Serial.print(".");
dot();
}
// Transmit the letter 'O' (---): three dashes
void letterO() {
Serial.print("-");
dash();
delay(interElementGap);
Serial.print("-");
dash();
delay(interElementGap);
Serial.print("-");
dash();
}
// Play the complete SOS sequence
void playSOS() {
Serial.print("Transmitting S: ");
letterS();
Serial.print(" | ");
delay(interLetterGap);
Serial.print("Transmitting O: ");
letterO();
Serial.print(" | ");
delay(interLetterGap);
Serial.print("Transmitting S: ");
letterS();
Serial.println();
Serial.println("SOS sequence transmission complete.");
}
Code Analysis
-
Pin Definitions: Uses
const intto define the pin numbers for the LED and the buzzer, making management and modification convenient.const int ledPin = 7;
const int buzzerPin = 8; -
Morse Code Timing Definitions: Defines the base time unit
dotDuration(dot). All other time intervals (dash, gaps) are calculated based on this. Note that the unit for the Arduinodelay()function is milliseconds, so all time units here are in milliseconds.const int dotDuration = 200; // Duration of a "dot" (1t)
const int dashDuration = dotDuration * 3; // Duration of a "dash" (3t)
const int interElementGap = dotDuration; // Gap between signals within the same letter (1t)
const int interLetterGap = dotDuration * 3; // Gap between letters (3t)
const int interWordGap = dotDuration * 7; // Gap between SOS sequences (7t) -
Initialization (
setup):Serial.begin(115200): Initializes serial communication for printing debug information to the serial monitor.pinMode(pin, OUTPUT): Configures the LED and buzzer pins as OUTPUT mode.signalOff(): Ensures the devices are in the OFF state when the program starts.
-
Main Loop (
loop):playSOS(): Calls the function to play the complete SOS signal.delay(interWordGap): Waits for the specified interval after each SOS sequence before repeating.
-
Basic Control Functions:
-
signalOn()/signalOff(): Encapsulates thedigitalWriteoperation to control the HIGH/LOW level of both the LED and buzzer simultaneously.The active buzzer used in this project has the characteristic of sounding whenever it is powered (GPIO outputs HIGH) and stopping when power is cut (GPIO outputs LOW).
-
dot()/dash(): Implement the signal logic for a "dot" and a "dash" respectively, controlling the duration of light/sound.
-
-
Letter Functions:
letterS()andletterO()combine calls todot()anddash()to form the corresponding letters and handle the small gaps (interElementGap) between signals within the letter. -
Play Function:
playSOS()calls the letter functions in the S-O-S order and inserts the longer gap (interLetterGap) between letters.