Section 7 Drive Peripheral
In this section, you will learn about the commonly used peripherals of the ESP32-S3 chip, the pin multiplexing and remapping mechanisms (IO MUX & GPIO Matrix), the general development workflow for peripheral drivers, and how to find and utilize official documentation resources for development.
1. Peripheral Overview
ESP32 series chips integrate a rich set of peripheral interfaces, enabling efficient communication with external devices such as sensors, displays, and storage devices. This facilitates core functions like data acquisition, signal control, information transfer, and image transmission.
However, due to differences in hardware design, the peripheral characteristics vary among different chip models, including the number of peripherals, GPIO pin multiplexing capabilities, and remapping support. Specific differences can be checked via the corresponding technical specifications found in the ESP Chip & Module Selector Tool.
This article will use the ESP32-S3 chip as an example.
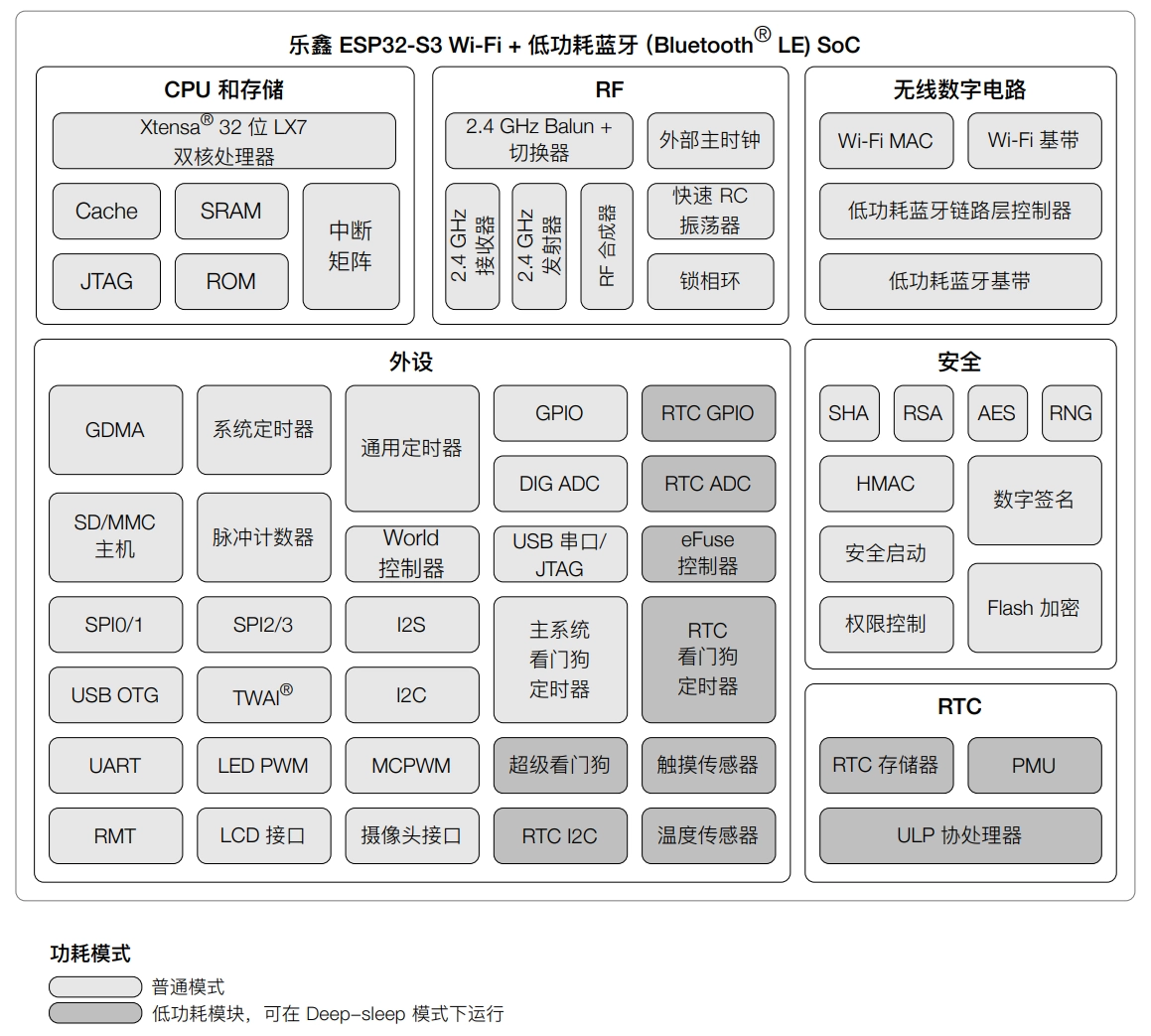
The following table covers the core purposes of commonly used peripherals.
| Peripheral | Purpose |
|---|---|
| LEDC | Multi-channel PWM output for dimming, speed control, etc. |
| I2C | Two-wire serial communication for connecting sensors, memory, etc. |
| SPI | High-speed full-duplex communication for connecting Flash, displays, sensors, etc. |
| UART | Serial port communication for debugging and peripheral data transmission/reception |
| ADC | Analog signal acquisition |
| I2S | Audio/multimedia data transfer, supporting full-duplex/half-duplex |
| LCD_CAM | Parallel LCD/camera interface for video data transfer |
| RMT | Infrared remote control, pulse signal transmission/reception |
| TWAI(CAN) | Automotive CAN communication |
| Touch | Onboard capacitive touch sensors |
| USB-OTG | USB communication (e.g., USB 2.0 OTG) |
| USB/JTAG | Debugging and downloading interface |
2. IO MUX and GPIO Matrix
The ESP32-S3 chip features 45 physical General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) pins. Each pin can be used as GPIO or to connect internal peripherals. Through the GPIO Matrix, IO MUX, and RTC IO MUX, the input signals of peripheral modules can be configured to come from any GPIO pin, and the output signals of peripheral modules can also be routed to any GPIO pin. These modules together form the chip's input/output control system.
IO MUX (Input/Output Multiplexer) and the GPIO Matrix are the two core mechanisms in the ESP32 series chips for achieving pin multiplexing and flexible peripheral signal assignment.
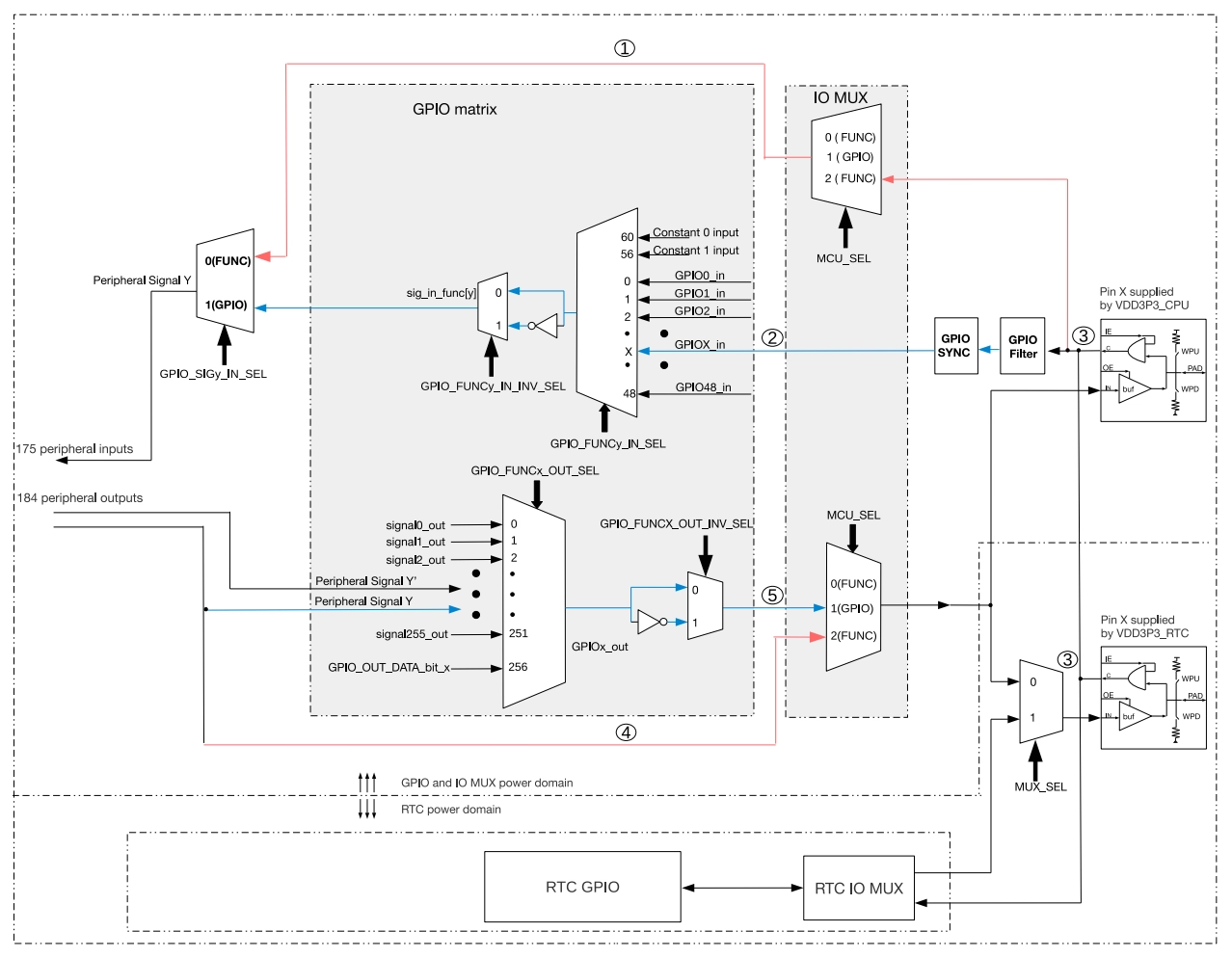
2.1 IO MUX
IO MUX is an internal multiplexer within the chip, allowing the same pin to perform different functions at different times.
Each pin can be configured for different functions via IO_MUX registers. Each pin can be selected through IO MUX:
- Direct signals from high-speed peripherals (such as SPI, JTAG, UART, etc.) for better high-frequency performance, though with less flexibility.
- Signals from the GPIO Matrix.
Typical Application:
For high-speed signals like those on an SPI bus, it is recommended to use pins directly connected via IO MUX to achieve the highest clock frequency and minimal latency.
2.2 GPIO Matrix
The GPIO Matrix is a hardware structure that allows the input/output signals of peripherals to be dynamically mapped to any available GPIO pin, providing flexibility in pin function assignment. Through the GPIO Matrix, a peripheral's input signal can come from any GPIO pin, and its output signal can also be routed to any GPIO pin.
Features:
- The input/output signals of most peripherals can be mapped to any GPIO via the GPIO Matrix.
- High flexibility, facilitating hardware design and avoiding pin conflicts.
- Introduces some signal delay and has frequency limitations for high-speed signals (e.g., up to 40MHz for SPI, and up to 80MHz for IO_MUX). For details, refer to the ESP-IDF SPI Master Driver Documentation.
Typical Application:
Peripherals like I2C, UART, PWM, and LED control can be freely assigned to any supported GPIO via the GPIO Matrix.
3. General Peripheral Development Workflow
- Include Headers and Driver Libraries: e.g.,
driver/gpio.h,driver/i2c_master.h - Declare Dependencies in CMakeLists.txt or idf_component.yml
- Configure Initialization Structures: e.g.,
gpio_config_t,i2c_master_bus_config_t - Call Initialization Functions: e.g.,
gpio_config(),i2c_new_master_bus(),i2c_master_bus_add_device() - Operate the Peripheral: e.g.,
gpio_set_level(),i2c_master_transmit(),i2c_master_transmit_receive() - Release Resources: e.g., unload I2C driver
4. Peripheral Development Documentation Resources
To develop for a specific peripheral, it is recommended to consult the following materials (using the ESP32-S3-Zero development board as an example):
- ESP32-S3 Datasheet: Understand the types of peripherals supported by the chip, key parameters, and basic features.
- ESP32-S3 Technical Reference Manual: Detailed usage methods, register descriptions, and configuration guides for various peripherals (e.g., UART, I2C, I2S, SPI, LCD, Camera).
- ESP-IDF Programming Guide: Find API usage, driver examples, and development workflows for peripherals. Suitable for beginners to get started quickly.
- Development Board User Manual/Schematic: Understand the specific pin assignments and hardware connections for peripherals on the development board to avoid hardware conflicts.
- Peripheral Examples and Components: ESP-IDF includes a rich set of peripheral example code and case studies explaining common peripheral uses and considerations.
- ESP32 Official FAQ: The official FAQ summarizes common issues, configuration methods, and considerations in peripheral development, suitable for finding answers to specific problems. - ESP-FAQ Peripherals
These resources can help you quickly identify key points in peripheral development. Combining them with official example code yields better results. If you have questions, you can also visit the ESP32 Forum to engage with the community.