Traffic Light
The core logic of this tutorial applies to all ESP32 boards, but all the operation steps are explained using the example of the Waveshare ESP32-S3-Zero mini development board. If you are using a development board of another model, please modify the corresponding settings according to the actual situation.
Project Introduction
This project demonstrates a traffic light simulation program. It controls three LED lights using the ESP32's GPIO pins, simulating the switching process of traffic light red, yellow, and green lights.
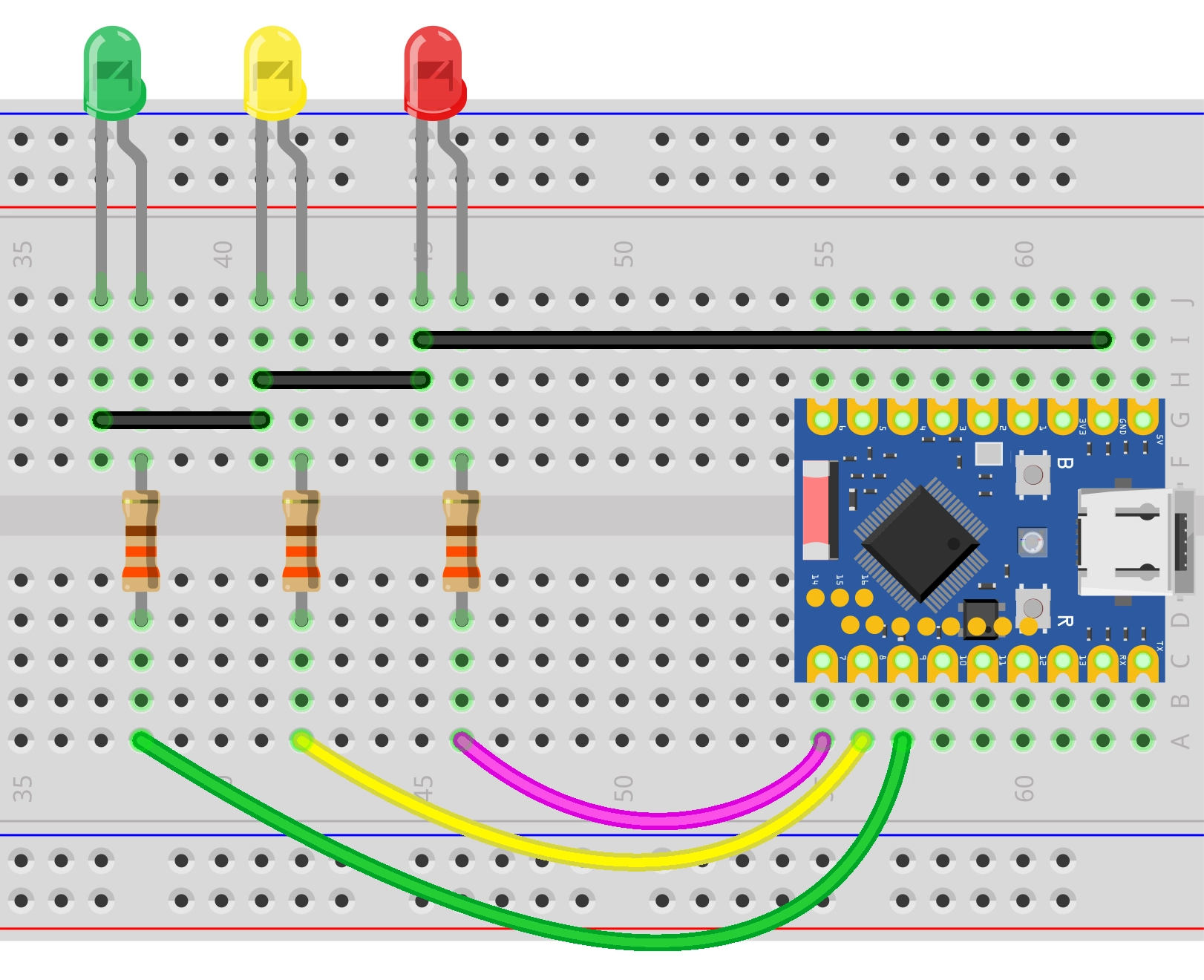
Hardware Connection
Components required:
- LED * 3
- 330Ω resistor * 3
- Breadboard * 1
- Wires
- ESP32 development board
Connect the circuit according to the wiring diagram below:
ESP32-S3-Zero Pinout Diagram

Code Implementation
import time
import machine
# Define the GPIO pin numbers connected to the red, yellow, and green LEDs
RED_LED_PIN = 7
YELLOW_LED_PIN = 8
GREEN_LED_PIN = 9
# Define the duration for each light phase
RED_LIGHT_DURATION = 10 # Red light stays on for 10 seconds
GREEN_LIGHT_DURATION = 8 # Green light stays on for 8 seconds
YELLOW_LIGHT_DURATION = 3 # Yellow light phase lasts for 3 seconds total
YELLOW_BLINK_INTERVAL = 0.5 # Yellow light blinking interval
# Initialize LED pins as output mode
red_led = machine.Pin(RED_LED_PIN, machine.Pin.OUT)
yellow_led = machine.Pin(YELLOW_LED_PIN, machine.Pin.OUT)
green_led = machine.Pin(GREEN_LED_PIN, machine.Pin.OUT)
def all_lights_off():
"""A helper function to turn off all LEDs."""
red_led.off()
yellow_led.off()
green_led.off()
# Program starts
print("Traffic light simulation program starting...")
print(f"Configuration: Red={RED_LIGHT_DURATION}s, Green={GREEN_LIGHT_DURATION}s, Yellow={YELLOW_LIGHT_DURATION}s")
print(f"Yellow light blink interval: {YELLOW_BLINK_INTERVAL}s")
try:
# Create an infinite loop to simulate the continuous operation of the traffic light
while True:
# --- Green Light Phase ---
print("Green light ON")
All_lights_off() # First turn off all lights to ensure a clean state
green_led.on() # Turn on the green light
time.sleep(GREEN_LIGHT_DURATION) # Wait for the configured green light time
# --- Yellow Blinking Phase ---
print("Yellow light blinking")
green_led.off() # Turn off the green light
# Calculate how many times the yellow light should blink within the specified total yellow duration
# A complete blink cycle is (ON + OFF), with a duration of YELLOW_BLINK_INTERVAL * 2
# Divide the total duration by a single cycle duration to get the number of blinks
num_blinks = int(YELLOW_LIGHT_DURATION / (YELLOW_BLINK_INTERVAL * 2))
# Ensure it blinks at least once even if the total time set is very short
if num_blinks == 0:
num_blinks = 1
for _ in range(num_blinks):
yellow_led.on() # Turn on the yellow light
time.sleep(YELLOW_BLINK_INTERVAL) # Stay on for a while
yellow_led.off() # Turn off the yellow light
time.sleep(YELLOW_BLINK_INTERVAL) # Stay off for a while
# Ensure the yellow light is off before entering the red light phase
yellow_led.off()
# --- Red Light Phase ---
print("Red light ON")
# At this point, the yellow and green lights are already off, just turn on the red light
red_led.on()
time.sleep(RED_LIGHT_DURATION) # Wait for the configured red light time
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("\n Program interrupted by user.")
finally:
# Whether the program ends normally or is interrupted, ensure all lights are turned off
all_lights_off()
print("All traffic lights are off. Program ended.")
Code Analysis
-
Import Libraries: The
machinelibrary is used for hardware control, and thetimelibrary is used for implementing delays. -
Constant Definitions: The beginning of the program defines GPIO pin numbers (
RED_LED_PIN, etc.) and the duration for each light phase (RED_LIGHT_DURATION, etc.). Centralizing these parameters facilitates quick adjustments based on actual needs without delving deep into modifying logic code.# Define the GPIO pin numbers connected to the red, yellow, and green LEDs
RED_LED_PIN = 7
YELLOW_LED_PIN = 8
GREEN_LED_PIN = 9
# Define the duration for each light phase
RED_LIGHT_DURATION = 10 # Red light stays on for 10 seconds
GREEN_LIGHT_DURATION = 8 # Green light stays on for 8 seconds
YELLOW_LIGHT_DURATION = 3 # Yellow light phase lasts for 3 seconds total
YELLOW_BLINK_INTERVAL = 0.5 # Yellow light blinking interval -
Pin Initialization: The
machine.Pinclass is used to create three objects corresponding to the red, yellow, and green lights. Themachine.Pin.OUTparameter configures the pins as output mode, allowing the program to control their high/low levels.# Initialize LED pins as output mode
red_led = machine.Pin(RED_LED_PIN, machine.Pin.OUT)
yellow_led = machine.Pin(YELLOW_LED_PIN, machine.Pin.OUT)
green_led = machine.Pin(GREEN_LED_PIN, machine.Pin.OUT) -
Helper Function: The
all_lights_off()function is used to turn off all LEDs simultaneously. Calling this function before state transitions ensures no light is accidentally on, improving the robustness of the code.def all_lights_off():
"""A helper function to turn off all LEDs."""
red_led.off()
yellow_led.off()
green_led.off() -
Main Loop Logic: The program executes three phases sequentially within an infinite loop
while True:- Green Light Phase: First, call
all_lights_off()to clear the state, turn on the green light, and delay forGREEN_LIGHT_DURATIONseconds. - Yellow Blinking Phase: Calculate the number of blinks (total duration divided by single cycle duration). Control the yellow light to alternately turn on and off through a
forloop to simulate a warning effect. - Red Light Phase: Turn on the red light and delay for
RED_LIGHT_DURATIONseconds. Since the yellow light was turned off at the end of the previous phase, simply turning on the red light is sufficient here.
- Green Light Phase: First, call
-
Exception Handling: The
try...except...finallystructure enhances program stability.except KeyboardInterrupt: Catches user interrupt signals (e.g., Ctrl+C), allowing the program to exit gracefully.finally: Executesall_lights_off()to turn off all lights whether the program ends normally or is interrupted, preventing the hardware from being left in an uncertain state.