SOS Signal
The core logic of this tutorial applies to all ESP32 boards, but all the operation steps are explained using the example of the Waveshare ESP32-S3-Zero mini development board. If you are using a development board of another model, please modify the corresponding settings according to the actual situation.
Project Introduction
This project demonstrates an SOS signal simulation program. It controls an LED and a buzzer via the ESP32's GPIO pins to simulate the SOS signal in Morse code.
Morse Code
First, let's understand the composition rules of Morse Code. Morse code uses different sequences to represent various English letters, numbers, and punctuation marks. It mainly consists of two basic signals:
- Dot: A short signal, denoted as
. - Dash: A long signal, denoted as
-
This project simulates the internationally recognized distress signal SOS. Its encoding rules are as follows:
- S: Consists of 3 dots, i.e.,
... - O: Consists of 3 dashes, i.e.,
---
Therefore, the complete SOS signal transmission sequence is: ... --- ....
Time Interval Definitions:
After understanding the character composition, it is crucial to strictly adhere to the international standard timing ratios, which determine the numerical relationships of the variables in our code:
- Basic Unit: We define the duration of a "dot" as 1 time unit (1t).
- Dash Length: It is 3 times the length of a dot (3t).
- Interval Times:
- Intra-character: The interval between dots and dashes within the same letter is 1t.
- Inter-letter: The interval between letters is 3t.
- Inter-word: The interval between words (or SOS sequences) is 7t.
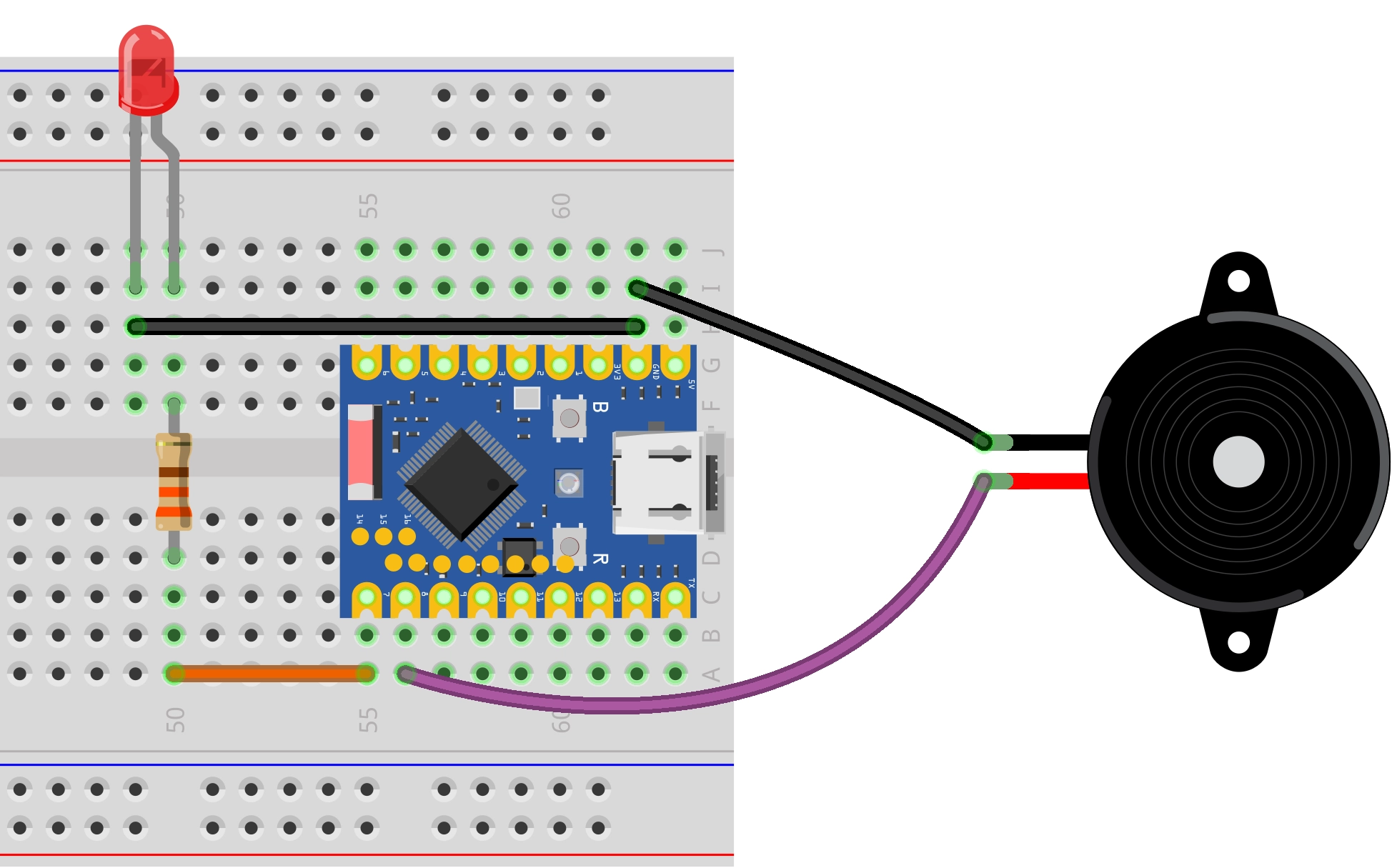
Hardware Connection
Components required:
- LED * 1
- 330Ω resistor * 3
- Active buzzer * 1
- Breadboard * 1
- Wires
- ESP32 development board
Connect the circuit according to the wiring diagram below:
ESP32-S3-Zero Pinout Diagram

Code Implementation
# Import necessary libraries
import time
import machine
# Define the pins connected to the LED and Buzzer
LED_PIN = 7 # LED
BUZZER_PIN = 8 # Buzzer
# Configure the pin numbers as output mode
led = machine.Pin(LED_PIN, machine.Pin.OUT)
buzzer = machine.Pin(BUZZER_PIN, machine.Pin.OUT)
# --- Morse Code Time Definitions ---
DOT_DURATION = 0.2 # Duration of a "dot" in seconds, serves as the base time unit
DASH_DURATION = 3 * DOT_DURATION # Dash = 3 dots
INTER_ELEMENT_GAP = DOT_DURATION # Intra-character gap = 1 dot
INTER_LETTER_GAP = 3 * DOT_DURATION # Inter-letter gap = 3 dots
INTER_WORD_GAP = 7 * DOT_DURATION # Inter-word gap = 7 dots
# --- Core Function Functions ---
def signal_on():
"""Turn on both the LED and the Buzzer simultaneously"""
led.on()
buzzer.on()
def signal_off():
"""Turn off both the LED and the Buzzer simultaneously"""
led.off()
buzzer.off()
def dot():
"""Send a "dot" signal"""
signal_on()
time.sleep(DOT_DURATION)
signal_off()
def dash():
"""Send a "dash" signal"""
signal_on()
time.sleep(DASH_DURATION)
signal_off()
def letter_s():
"""Send the letter 'S' (...): three dots"""
print('.', end='')
dot()
time.sleep(INTER_ELEMENT_GAP)
print('.', end='')
dot()
time.sleep(INTER_ELEMENT_GAP)
print('.', end='')
dot()
def letter_o():
"""Send the letter 'O' (---): three dashes"""
print('-', end='')
dash()
time.sleep(INTER_ELEMENT_GAP)
print('-', end='')
dash()
time.sleep(INTER_ELEMENT_GAP)
print('-', end='')
dash()
def play_sos():
"""Play one complete SOS signal sequence"""
print("Sending S: ", end='')
letter_s()
print(" | ", end='')
time.sleep(INTER_LETTER_GAP)
print("Sending O: ", end='')
letter_o()
print(" | ", end='')
time.sleep(INTER_LETTER_GAP)
print("Sending S: ", end='')
letter_s()
print()
print("SOS sequence sent.")
# --- Main Program ---
try:
print("Program starting, preparing to send SOS signal. Press Ctrl+C to stop.")
# Ensure devices are off in the initial state
signal_off()
time.sleep(2) # Wait 2 seconds before starting
# Infinite loop, continuously sending the SOS signal
while True:
play_sos()
# After one complete SOS sequence, wait for the interval
print(f"Waiting {INTER_WORD_GAP} seconds before repeating...\ n")
time.sleep(INTER_WORD_GAP)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
# When the user presses Ctrl+C, a KeyboardInterrupt exception is caught
print("\n Program interrupted by user.")
finally:
# This code executes whether the program ends normally or is interrupted
print("Turning off LED and buzzer...")
signal_off()
print("Devices safely shut down.")
Code Analysis
-
Import Libraries: The
machinelibrary is used for hardware control (GPIO), and thetimelibrary is used for implementing delays. -
Pin Definitions: The beginning of the program defines the GPIO pin numbers for the LED and buzzer.
# Define the pins connected to the LED and Buzzer
LED_PIN = 7 # LED
BUZZER_PIN = 8 # Buzzer -
GPIO Initialization: The
machine.Pinclass is used to create objects, configuring the pins asmachine.Pin.OUT(output mode) to control high/low levels.An active buzzer has an integrated oscillation source and operates on the principle of "sounds when powered" (it beeps whenever the GPIO outputs a high level), allowing control via digital signal output.
# Configure the pin numbers as output mode
led = machine.Pin(LED_PIN, machine.Pin.OUT)
buzzer = machine.Pin(BUZZER_PIN, machine.Pin.OUT) -
Morse Code Time Definitions: The base time unit
dot_duration(dot) is defined. All other time intervals (dash, gaps) are calculated based on this. This parameterized design makes it very easy to adjust the playback speed by modifying just one variable.# --- Morse Code Time Definitions ---
DOT_DURATION = 0.2 # Duration of a "dot" in seconds, serves as the base time unit
DASH_DURATION = 3 * DOT_DURATION # Dash = 3 dots
INTER_ELEMENT_GAP = DOT_DURATION # Intra-character gap = 1 dot
INTER_LETTER_GAP = 3 * DOT_DURATION # Inter-letter gap = 3 dots
INTER_WORD_GAP = 7 * DOT_DURATION # Inter-word gap = 7 dots -
Basic Control Functions:
signal_on()andsignal_off()encapsulate the synchronized control of the LED and buzzer.signal_on(): Simultaneously lights the LED and activates the buzzer.signal_off(): Simultaneously turns off the LED and the buzzer.
-
Morse Code Elements: The
dot()anddash()functions implement the transmission of "dot" and "dash" signals, respectively. They both automatically callsignal_off()after sending the signal, ensuring the state is clear before the next signal begins. -
Letter Functions:
letter_s()andletter_o()represent the letters S (...) and O (---) by combining dots and dashes, strictly adhering to Morse code spacing standards. -
Main Loop Logic:
- The
play_sos()function plays the complete distress signal in the order S-O-S. - The
while Trueloop ensures the signal is sent repeatedly, waitinginter_word_gapseconds after each transmission.
- The
-
Exception Handling: The
try...except...finallystructure enhances program stability.except KeyboardInterrupt: Catches a user interrupt (Ctrl+C), allowing the program to exit gracefully.finally: Regardless of how the program ends, it forces a call tosignal_off()to shut down the devices, preventing the buzzer from sounding continuously or the LED from staying on.