Weather Display
The core logic of this tutorial applies to all ESP32 development boards. However, all operational steps are explained using the Waveshare ESP32-S3-Zero Mini Development Board as an example. If you are using a different model of development board, please modify the relevant settings according to your actual situation.
Project Introduction
This project demonstrates how to create a Network Weather Display using an ESP32. By connecting to a Wi-Fi network, the ESP32 will periodically fetch real-time weather data (weather conditions and temperature) for a specified city from the Seniverse Weather API and display this information on a Waveshare 1.5inch OLED screen.
Hardware Connection
The components required are:
- Waveshare 1.5inch OLED Module * 1
- Breadboard * 1
- Wire
- ESP32 development board
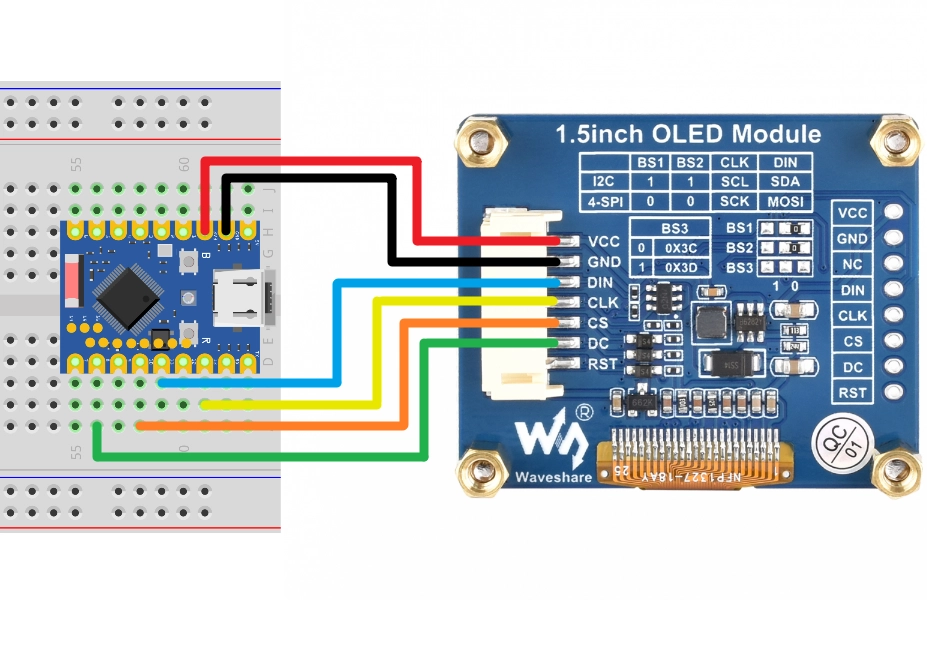
Connect the circuit according to the wiring diagram below:
ESP32-S3-Zero Pinout Diagram

This example uses the SPI interface to connect to the OLED display. This screen also supports I2C, controlled via the BS1 and BS2 jumpers. If you are using I2C mode, please refer to the wiring method described in Section 7 I2C Communication.
| ESP32 Pin | OLED Module | Description |
|---|---|---|
| GPIO 13 | SCK | SPI Clock Line |
| GPIO 11 | MOSI | SPI Data Output |
| GPIO 10 | CS | Chip Select Signal |
| GPIO 8 | DC | Data/Command Select |
| 3.3V | VCC | Power Positive |
| GND | GND | Power Ground |
Code Implementation
This code example depends on the following libraries. Please install it via the Arduino IDE Library Manager:
- Adafruit SSD1327 (for driving the OLED screen)
- Adafruit GFX Library (core graphics library)
- ArduinoJson (for parsing JSON data)
/*
WiFi Weather Display
This example demonstrates how to connect to Wi-Fi, fetch weather data in JSON format via HTTP, and display it on an SSD1327 OLED screen.
API Provider: Seniverse Weather
Circuit Connection:
- OLED SCK -> GPIO 13
- OLED MOSI -> GPIO 11
- OLED CS -> GPIO 10
- OLED DC -> GPIO 8
Wulu (Waveshare Team)
*/
#include <WiFi.h>
#include <HTTPClient.h>
#include <ArduinoJson.h>
#include <Adafruit_GFX.h>
#include <Adafruit_SSD1327.h>
// Wi-Fi Configuration (Please replace with your Wi-Fi credentials)
const char* ssid = "Maker";
const char* password = "12345678";
// Seniverse Weather API Configuration (Please replace with your private key)
String apiKey = "SIAJmsAgSAiBZfefH";
// The city for which you want to query the weather
String location = "shenzhen";
// API URL Template
const String apiUrlTemplate = "https://api.seniverse.com/v3/weather/now.json?key=%s&location=%s&language=en&unit=c";
// Update interval: 30 minutes (in milliseconds)
const unsigned long updateInterval = 1800000;
unsigned long lastUpdateTime = 0;
// SPI Pin Configuration
const int SCK_PIN = 13;
const int MOSI_PIN = 11;
const int CS_PIN = 10;
const int DC_PIN = 8;
// Initialize OLED (SPI)
// 128x128 resolution
Adafruit_SSD1327 display(128, 128, &SPI, DC_PIN, -1, CS_PIN);
// If using I2C, please use the following constructor (I2C address needs to be confirmed, usually 0x3D)
// const int SDA_PIN = 2;
// const int SCL_PIN = 1;
// Adafruit_SSD1327 display(128, 128, &Wire, -1); // -1 indicates no reset pin
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
// Wire.begin(SDA_PIN, SCL_PIN);
// Initialize OLED (I2C)
// if (!display.begin(0x3D)) {
// Serial.println("Unable to initialize OLED");
// while (true) yield();
// }
SPI.begin(SCK_PIN, -1, MOSI_PIN, CS_PIN);
// Initialize OLED
if (!display.begin()) {
Serial.println("Unable to initialize OLED");
while (true) yield();
}
// Set text size and color
display.setTextSize(1);
display.setTextColor(SSD1327_WHITE);
display.clearDisplay();
display.display();
connectWiFi();
// Initial weather fetch
getWeather();
lastUpdateTime = millis();
}
void loop() {
// Timed updates
if (millis() - lastUpdateTime >= updateInterval) {
getWeather();
lastUpdateTime = millis();
}
}
void connectWiFi() {
// Connect to Wi-Fi
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA);
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
Serial.print("Connecting to WiFi");
display.clearDisplay();
display.setCursor(5, 20);
display.print("Connecting to");
display.setCursor(5, 40);
display.print("WiFi...");
display.display();
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println("\nConnected!");
Serial.print("IP Address: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
display.clearDisplay();
display.setCursor(5, 20);
display.print("WiFi Connected!");
display.setCursor(5, 40);
display.print("IP:");
display.setCursor(5, 55);
display.print(WiFi.localIP());
display.display();
delay(2000);
}
void displayWeather(String city, String weather, String temperature) {
display.clearDisplay();
display.setTextSize(1);
display.setTextColor(SSD1327_WHITE);
// City name
display.setCursor(5, 10);
display.print("City: ");
display.println(city);
// Weather condition
display.setCursor(5, 40);
display.println("Weather:");
display.setCursor(5, 55);
display.println(weather);
// Temperature
display.setCursor(5, 85);
display.print("Temp: ");
display.print(temperature);
display.println(" C");
display.display();
Serial.printf("Display updated: %s, %s, %s C\n", city.c_str(), weather.c_str(), temperature.c_str());
}
void getWeather() {
if (WiFi.status() == WL_CONNECTED) {
HTTPClient http;
// Build the complete request URL
char url[200];
sprintf(url, apiUrlTemplate.c_str(), apiKey.c_str(), location.c_str());
Serial.print("Fetching weather from: ");
Serial.println(url);
display.clearDisplay();
display.setCursor(5, 20);
display.print("Fetching...");
display.display();
http.begin(url);
int httpCode = http.GET();
if (httpCode > 0) {
if (httpCode == HTTP_CODE_OK) {
String payload = http.getString();
Serial.println("API Response:");
Serial.println(payload);
// Parse JSON
JsonDocument doc;
DeserializationError error = deserializeJson(doc, payload);
if (!error) {
JsonObject result = doc["results"][0];
String locationName = result["location"]["name"].as<String>();
String weatherText = result["now"]["text"].as<String>();
String temperature = result["now"]["temperature"].as<String>();
displayWeather(locationName, weatherText, temperature);
} else {
Serial.print("deserializeJson() failed: ");
Serial.println(error.c_str());
displayWeather("Error", "JSON Fail", "");
}
} else {
Serial.println("API Error: " + http.getString());
}
} else {
Serial.printf("HTTP GET failed, error: %s\n", http.errorToString(httpCode).c_str());
displayWeather("Error", "HTTP Fail", "");
}
http.end();
} else {
Serial.println("WiFi Disconnected");
// Attempt to reconnect
connectWiFi();
}
}
Code Analysis
-
Library Imports:
WiFi.h: ESP32's Wi-Fi library for network connectivity.HTTPClient.h: For sending HTTP requests.ArduinoJson.h: A powerful JSON parsing library for processing API response data.Adafruit_GFX.handAdafruit_SSD1327.h: Graphics and SSD1327 driver libraries provided by Adafruit for controlling the OLED display.
-
Configuration Parameters:
ssidandpassword: Wi-Fi network credentials.apiKeyandlocation: Seniverse Weather API key and city setting.SCK_PIN,MOSI_PIN, etc.: Define the pin connections for the SPI interface.
-
Object Initialization:
Adafruit_SSD1327 display(...): Creates the display object. This example uses hardware SPI mode (passing&SPI). In thesetup()function, the SPI pin mapping is customized viaSPI.begin(SCK_PIN, -1, MOSI_PIN, CS_PIN). If you need to use I2C mode, please refer to the commented section in the code.
-
connectWiFi()Function:- Initiates connection using
WiFi.begin(). - Checks connection status with
WiFi.status()until successful. - Displays connection progress and the obtained IP address on the screen in real-time.
- Initiates connection using
-
getWeather()Function:- Constructs the API request URL.
- Sends the request using
http.GET(). - Upon receiving the response, parses the JSON data using
deserializeJson(). - Extracts fields like
location,text(weather condition),temperature. - Calls
displayWeather()to update the display.
-
displayWeather()Function:- Clears the screen using
display.clearDisplay(). - Uses
display.setCursor()anddisplay.print()to display text information at specified positions. display.display()sends the buffer contents to the screen for display.
- Clears the screen using
-
loop()Function:- Uses
millis()for non-blocking timing, callinggetWeather()every 30 minutes (updateInterval) to update weather information.
- Uses